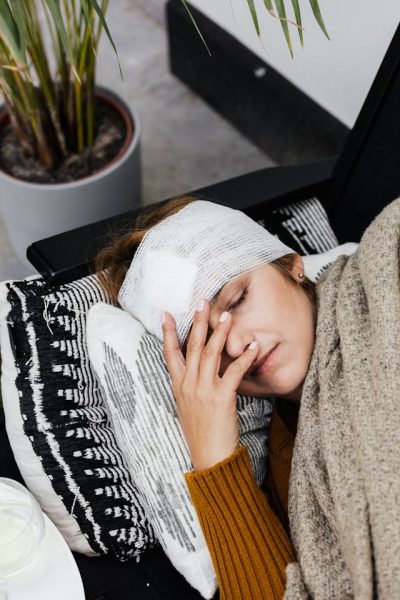
Nearly one-third of people suffer a concussion at some point in their lives. This movement can damage brain cells and affect how the brain functions. Concussions are usually not life-threatening but can cause complications if not treated well.
Understanding a Concussion
A concussion is a brain injury that occurs when the head is jolted or hit by a hard object. A blow to the body can also cause the head and brain to jerk back and forth rapidly, leading to a concussion. The rapid movement changes the shape of brain tissue and causes damage to the brain cells. The resulting cellular damage from concussions triggers chemical and metabolic brain changes that affect the way cells function and communicate.
Given that the brain is the body’s main control system, the effects of concussions can lead to many physical, emotional, and cognitive changes.
Concussions are unusually not life-threatening, but it’s good to treat them seriously. Failure to address concussion symptoms or seek proper medical treatment can lead to serious brain damage with potential long-term effects.
Common Causes of Concussions
The brain is made of soft tissue. It’s cushioned by spinal fluid, while the skull provides an external protective shell. A blow to the head can make your brain shift inside the skull. This causes bruising, damage to blood vessels, and nerve injuries.
Factors that increase your risk of a concussion include:
- Falls: Falling remains the primary cause of concussions among both young children and older adults. You can get a concussion when you fall down, and your head hits the ground or a hard object.
- Sports injuries: Football, soccer, hockey, and basketball players are at a higher risk of getting concussions. When another player strikes your head or when you get hit by a ball, it may lead to brain trauma.
- Car accidents: Car crashes often cause concussions due to the sudden impact or rapid movement of the head. Even if there is no direct head injury, the brain can still hit the inside of the skull due to the sudden stop.
- Physical assault: A concussion may result from any physical violence, including punches or being hit with an object. Concussions happen mostly in domestic violence cases and physical fights.
- Explosive blasts: Military personnel who encounter explosions can develop concussions because of shockwave exposure. The blasts generate intense pressure, which disrupts brain function.
What Are the Symptoms of Concussion?
Concussions can be tricky to diagnose. Even if you have visible cuts or bruises on your head, it does not mean you have a concussion. It’s also worth noting that the symptoms of a concussion may not develop until days or weeks after the injury. Concussion symptoms can also disappear in seconds, while others may linger.
That said, it’s important to know how to recognize the signs and symptoms of concussions so you can take immediate action. Some of the most common symptoms of a concussion include:
- Headache or pressure in the head
- Dizziness or balance problems
- Blurred vision
- Confusion or trouble concentrating.
- Memory loss
- Nausea or vomiting
- Sensitivity to light or noise
- Feeling tired or sluggish
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms after a head injury, it is important to seek medical attention.
How Long Does a Concussion Last?
Concussions typically resolve within a few weeks but can persist for up to a month. However, people respond to concussions differently, and therefore, the recovery time varies from one person to another. That said, the time needed for your brain to recover from a concussion depends on several different factors, including:
- What caused the concussion?
- If you experienced any other injuries.
- If you develop any complications.
- How severe the symptoms you experience are.
Make sure to consult your healthcare provider before going back to your daily activities. Also, don’t start exercising or playing sports until your healthcare provider gives you permission to do so. The healing process of your brain occurs naturally and the best thing you can do is rest and give it time.
How to Prevent Concussions
While concussions are not always avoidable, you can take certain steps to reduce the risk:
- Wear protective gear when playing sports.
- Use seat belts while driving and ensure airbags are functional.
- Keep living spaces free from tripping hazards.
- Use helmets when riding bikes, motorcycles, or skateboards.
- Be extra-careful in slippery or uneven areas.
Protect Your Brain
A concussion may seem like a minor injury, but it can have lasting effects if not taken seriously. You can protect yourself and your loved ones by understanding what causes concussions. If you suspect you have a concussion, seek medical attention so you can properly recover.