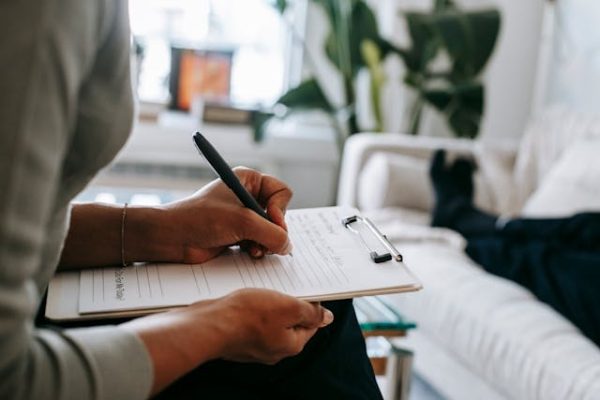
When it comes to mental health treatments, several factors can influence how people respond. Biological, psychological, and social determinants play significant roles in this process. Your genetics might affect how you metabolize certain medications, while your psychological resilience could impact how therapies work for you. Additionally, social factors such as support systems and community resources can be key in determining the success of mental health interventions.
Cultural influences are also a key consideration. In mental health treatment, cultural sensitivity is important because it guarantees that mental health services are tailored to meet diverse needs. Understanding and respecting these cultural nuances can help deliver more effective care and avoid misdiagnoses due to cultural misunderstandings.
Navigating mental health treatment can be complex, yet options are becoming more accessible. For instance, obtaining an online prescription for Lexapro can offer more flexibility and convenience for many individuals seeking treatment. As you explore these avenues, recognize the importance of these diverse factors to make informed decisions about your mental health care.
Biological and Genetic Factors
Various biological and genetic factors can influence your response to mental health treatments. These include levels of neurotransmitters and hormones, genetic predispositions, and the structure and functionality of your brain.
Neurotransmitter and Hormonal Levels
The balance of neurotransmitters and hormones in your body plays a key role in mental health. Neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine affect mood and behavior. When levels are off, it can lead to conditions such as depression or anxiety. Hormones like cortisol also have an impact. High cortisol levels often relate to stress and can affect how your body responds to treatment. Maintaining this balance is important for achieving effective treatment results.
Short Paragraph: Disruptions in neurotransmitter levels can be influenced by genetics, environmental factors, or lifestyle. This disruption might affect how you respond to medications that balance these chemicals.
Genetic Predispositions
Your genetic makeup can predispose you to certain mental health conditions, influencing treatment outcomes. Research has shown that mental disorders often run in families, suggesting a genetic link. Specific genes may increase the risk for conditions like depression or anxiety, affecting how you respond to therapies and medication. If you have a family history of mental health issues, it’s particularly important to consider genetic testing and counseling as part of your treatment plan.
Short Paragraph: Understanding your genetic background could provide insights into the most effective treatment options for you. Personalized medicine, which considers your unique genetic profile, may improve treatment outcomes.
Brain Structure and Functionality
Variations in brain structure and function can also affect how you respond to mental health treatments. Changes in areas of the brain involved in mood regulation, such as the prefrontal cortex and amygdala, can influence the effectiveness of treatments. Advanced imaging techniques allow researchers to study these structures and their connections, helping to customize treatments based on individual brain characteristics.
Short Paragraph: By examining brain imaging results, healthcare providers can tailor therapies to suit your needs better. This approach targets specific areas with interventions like cognitive behavioral therapy or medication adjustments.
Psychosocial and Environmental Factors
Psychosocial and environmental factors can significantly affect how people respond to mental health treatments. Life events, family dynamics, and cultural attitudes are important in shaping an individual’s experience and treatment outcomes.
Life Events and Stressors
Life events, such as losing a job, moving to a new place, or experiencing personal loss, can greatly affect mental health. These events might increase stress and anxiety. How a person handles stress can impact the effectiveness of treatment. It’s common for stressors like financial struggles or relationship problems to influence mental well-being. Recognizing and managing these stressors can make treatment more effective. It is important for caregivers and professionals to consider these elements when tailoring treatments.
Family Dynamics and Support Systems
The support you receive from your family and friends can greatly affect mental health outcomes. A strong support system can make you feel understood and encouraged. This support can help you stick with treatment plans and achieve better results. On the other hand, a lack of support or negative family dynamics might hinder progress. Open communication and positive relationships are key. Recognizing family and friends’ roles can be important in the path to mental health recovery.
Cultural and Societal Attitudes
Cultural beliefs and societal attitudes can shape how you perceive and respond to mental health treatments. In some cultures, mental health issues may be stigmatized, making treatment more challenging to pursue. Understanding these cultural attitudes helps tailor treatments to be more respectful and effective. Being aware of societal norms and beliefs can guide you in overcoming barriers to accessing care. This understanding promotes a more inclusive approach to mental health care.
Conclusion
Understanding how people respond to mental health treatments involves several factors. Personal motivation plays a significant role as individuals must actively engage in their treatment to be effective.
Environmental factors, like support from family and friends, are also important. The type of treatment, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, impacts effectiveness.
Barriers like stigma and access to care influence treatment outcomes, too. Certain groups may find it harder to engage with mental health services due to these challenges.
Considering these factors can help improve treatment responses in mental health care. You can better manage mental health treatment plans by focusing on individual needs and addressing common barriers.