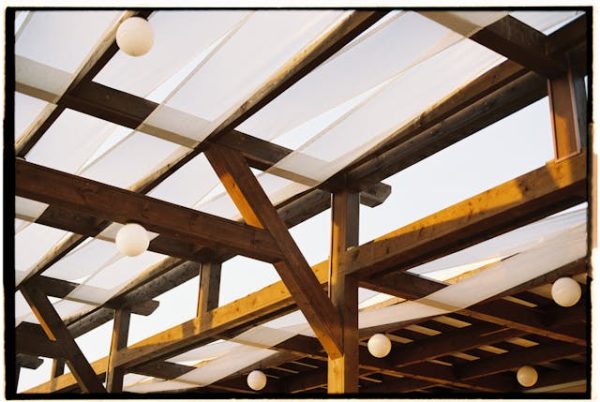
Outdoor shade has come a long way from simple canvas coverings stretched over wooden frames that protected storefronts and homes in earlier centuries. Those basic solutions served their purpose but offered little flexibility, required constant maintenance, and lacked the sophistication modern homeowners expect from outdoor living enhancements that cost thousands of dollars.
Today’s homeowners enjoy motorized awnings, climate sensors, and smart-home integrations that would’ve seemed like science fiction just decades ago. Technology transformed outdoor shade from purely functional sun protection into sophisticated systems responding intelligently to conditions and integrating seamlessly with connected homes that manage lighting, temperature, and security through unified platforms.
The journey of outdoor shade shows how innovation, materials, and technology have transformed the way we relax outside. Understanding this evolution helps appreciate modern capabilities while providing perspective on where outdoor shade technology might head next as smart homes become increasingly sophisticated and homeowner expectations continue rising.
From Manual Awnings to Motorized Systems
Early awnings required manual cranking using hand wheels connected to gears that extended and retracted fabric through pure mechanical advantage. These systems worked but demanded physical effort that became tedious, especially for larger awnings requiring dozens of cranks to fully extend or retract. Many homeowners simply left awnings in one position rather than bothering with constant adjustments.
Electric motors revolutionized convenience when they became affordable and reliable enough for residential applications in the late 20th century. Push-button operation eliminated cranking labor, making awning adjustments so easy that homeowners actually used retraction features rather than leaving awnings permanently extended or closed. This increased usage meant awnings lasted longer by avoiding constant weather exposure.
Remote controls and wall switches evolved quickly, giving homeowners multiple control points and eliminating the need to be directly at awnings for operation. Wireless remotes meant adjusting awnings from inside homes or across yards without walking to wall switches. This convenience continued driving increased awning usage as effort barriers dropped to essentially zero compared to earlier manual systems.
Weather Sensors and Automation for Smarter Control
Wind sensors detect dangerous gusts and automatically retract awnings before damage occurs, protecting investments that would otherwise tear or bend under forces exceeding design limits. These sensors eliminate reliance on homeowners remembering to retract during storms, preventing the damage that happens when people forget or aren’t home during unexpected weather events.
Sun sensors extend awnings automatically when sunlight reaches certain intensities, providing shade exactly when needed without homeowner intervention. This automation means porches stay comfortable throughout days as sun angles change without anyone thinking about adjustments. Smart shade that responds to actual conditions rather than fixed schedules adapts naturally to seasonal variations and weather patterns.
Rain sensors trigger retraction, preventing water accumulation on fabrics not designed for wet storage while retracted. Getting caught extended during rain doesn’t damage modern awnings, but retracting wet fabric can create mildew problems if moisture gets trapped. Sensors prevent this by ensuring awnings only retract dry or deploy protective measures when wet storage becomes necessary.
Sustainable Materials and Energy Efficiency
Modern fabrics using recycled materials and sustainable manufacturing processes appeal to environmentally conscious homeowners wanting shade solutions aligned with green values. Solution-dyed acrylics and recycled polyesters deliver performance without environmental guilt, addressing concerns that earlier synthetic fabrics raised about petroleum dependence and manufacturing waste.
Energy efficiency improvements from advanced awning systems reduce cooling costs substantially by preventing solar heat gain before it enters homes. Studies show properly deployed awnings cutting cooling costs 15-25%, making them effective passive cooling systems that pay for themselves through utility savings over several years. This energy efficiency positions awnings as green technology rather than just aesthetic upgrades.
Durability improvements mean modern awnings last decades rather than years, reducing replacement frequency and waste associated with shorter-lived products. Better UV resistance, mildew prevention, and structural engineering all contribute to longevity that makes awnings more sustainable through extended service lives. Buying once and using for 15-20 years beats replacing cheap awnings every 5 years from sustainability perspectives.
The Future: Integrated Shade and Smart Home Design
Voice control through Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri integrates awnings into smart home ecosystems where verbal commands adjust shade alongside lighting, temperature, and entertainment systems. Natural language control eliminates even the minimal effort of finding remotes or apps, making awning adjustment as simple as speaking desires aloud.
Smartphone apps provide remote control from anywhere, letting homeowners close awnings when storms approach, even while away from home, or extend them before arriving to pre-cool outdoor spaces. Geofencing automatically adjusts awnings based on whether homeowners are home or away, optimizing shade for occupancy patterns without manual intervention.
Artificial intelligence learning usage patterns and preferences could enable awnings that anticipate needs before homeowners think about adjustments. Systems might learn that families prefer morning sun but afternoon shade, automatically adjusting throughout days without programming. Predictive automation represents the next frontier where outdoor shade becomes truly intelligent rather than just responsive to immediate conditions.
Conclusion
Connecting innovation to lifestyle improvement shows outdoor shade evolution from basic sun protection to sophisticated systems enhancing comfort, reducing energy costs, and integrating with modern smart homes. Understanding this progression helps appreciate current capabilities while anticipating future developments that will continue improving outdoor living experiences.
Readers should explore modern outdoor shade solutions that balance comfort, design, and technology rather than settling for basic systems when better options exist. Today’s shade technology delivers capabilities that justify investments through convenience, energy savings, and sophistication that earlier generations couldn’t imagine. Embracing these improvements means enjoying outdoor spaces more fully while benefiting from efficiency and automation that make shade management effortless.