Ceramics have played a significant role in European culture for centuries. Each region boasts unique techniques and styles.
Among these, Polish ceramics (also known as Polish pottery) stands out for its vivid patterns and durability.
This article dives deep into the distinct characteristics of Polish pottery compared to other renowned European ceramic traditions.
What Makes Polish Pottery Unique?
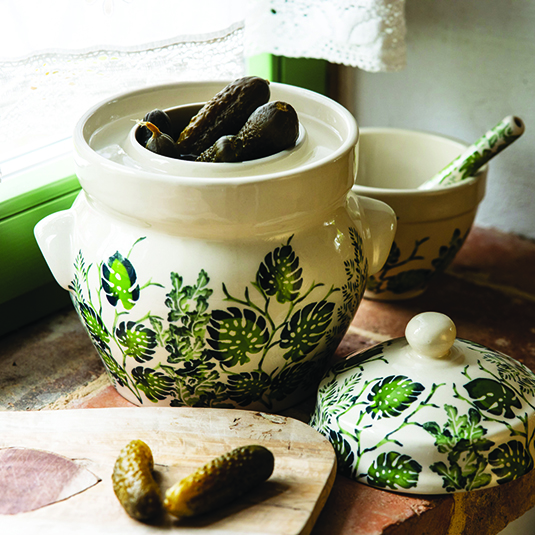
Polish pottery, especially from the Bolesławiec region, stands out for several reasons. Its style is easy to recognize with its intricate hand-painted designs. These designs often include dots, flowers, peacocks, and traditional folk art.
The main colors used are rich blues, greens, reds, and whites. These pieces are not only beautiful but also very functional and durable, making them perfect for baking and serving.
The process of making Polish pottery is quite special. Artisans use local clay known for its high mineral content, which makes it withstand high temperatures well.
The clay is formed by hand or with molds and then carefully hand-painted with sponges and brushes. Each piece is fired multiple times at very high temperatures to ensure it is strong and long-lasting.
Other European regions might focus more on different materials or glazing methods. While each region has its own unique style, Polish pottery stands out for its perfect blend of practical use and visual appeal.

How Does Italian Majolica Compare?
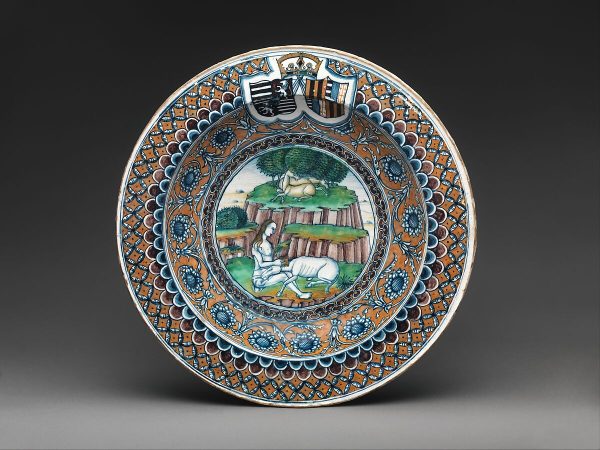
Italian Majolica is another interesting ceramic tradition that dates back to the Renaissance period.
Unlike Polish pottery, Majolica is known for its tin-glazed earthenware, which was initially made to look like Chinese porcelain’s bright white surface. Majolica pieces often feature scenes from history, the Bible, or pastoral life painted in vibrant colors on a white background.
The process of making Majolica is quite detailed and labor-intensive. Artisans start by shaping pots from terracotta clay. They then apply a lead glaze followed by a tin enamel coating, which allows for detailed painting before the final firing. This tin glaze gives Majolica its bright, varied color palette, unlike the earthy tones commonly found in Polish pottery.
Both Polish pottery and Italian Majolica involve detailed design and expert handcrafting, but they reflect different cultural traditions. Polish ceramics tend to highlight folk traditions and functional design, while Italian Majolica showcases the grandeur and complexity of Renaissance art.

Different Artistic Themes
Beyond the technical differences, the artistic themes in these pottery traditions are quite distinct. Polish pottery often highlights simple beauty and nature, featuring cheerful floral patterns. In contrast, Italian Majolica frequently illustrates complex stories and human figures.
Imagine a Majolica plate adorned with an intricate Renaissance scene versus a Polish ceramic dish decorated with lively flowers. Each piece tells its own story, but they do so in very different visual styles.
While Majolica dazzles with elaborate, historical narratives, Polish pottery charms with its straightforward, nature-inspired designs.
Is French Faience Similar or Different?
French Faience is another well-known European ceramic tradition and shares some similarities with Italian Majolica because both use tin-glazing techniques. However, French Faience has unique styles depending on the region within France, like Rouen, Nevers, and Marseille.

Faience usually features light backgrounds with vibrant decor elements in blue, yellow, and green. It emphasizes elegance and sophistication.
The process starts with finely ground clay shaped into the desired forms. After the first firing, an opaque white tin glaze is applied. Artists then paint intricate designs on this surface.
Common themes include classical mythology or chinoiserie, reflecting Europe’s historical fascination with Eastern art.
In terms of functionality, Faience is mostly decorative, unlike Polish pottery, which is designed to be both beautiful and practical for everyday use.
Reflecting Europe’s Cross-Cultural Influences
One interesting difference between French Faience and Polish pottery is the cross-cultural influences.
Faience often features oriental motifs, showing the impact of Europe’s historical trade routes and the blending of different artistic styles.
On the other hand, Polish pottery tends to stick to local folklore and traditions, with less influence from external sources over the centuries.
Why Choose One Over the Other?
It comes down to your personal preferences and what you need.
Are you looking for decorative pieces that showcase historical European artistry? Or do you want versatile kitchenware that combines function with traditional folk designs?
The charm of European ceramics lies in their diverse heritage. Each tradition brings its own mix of history, culture, and artistry, allowing collectors and enthusiasts to find pieces that truly match their tastes and needs.